The Most Effective Treatment for Depression
Understanding, Support, and Healing
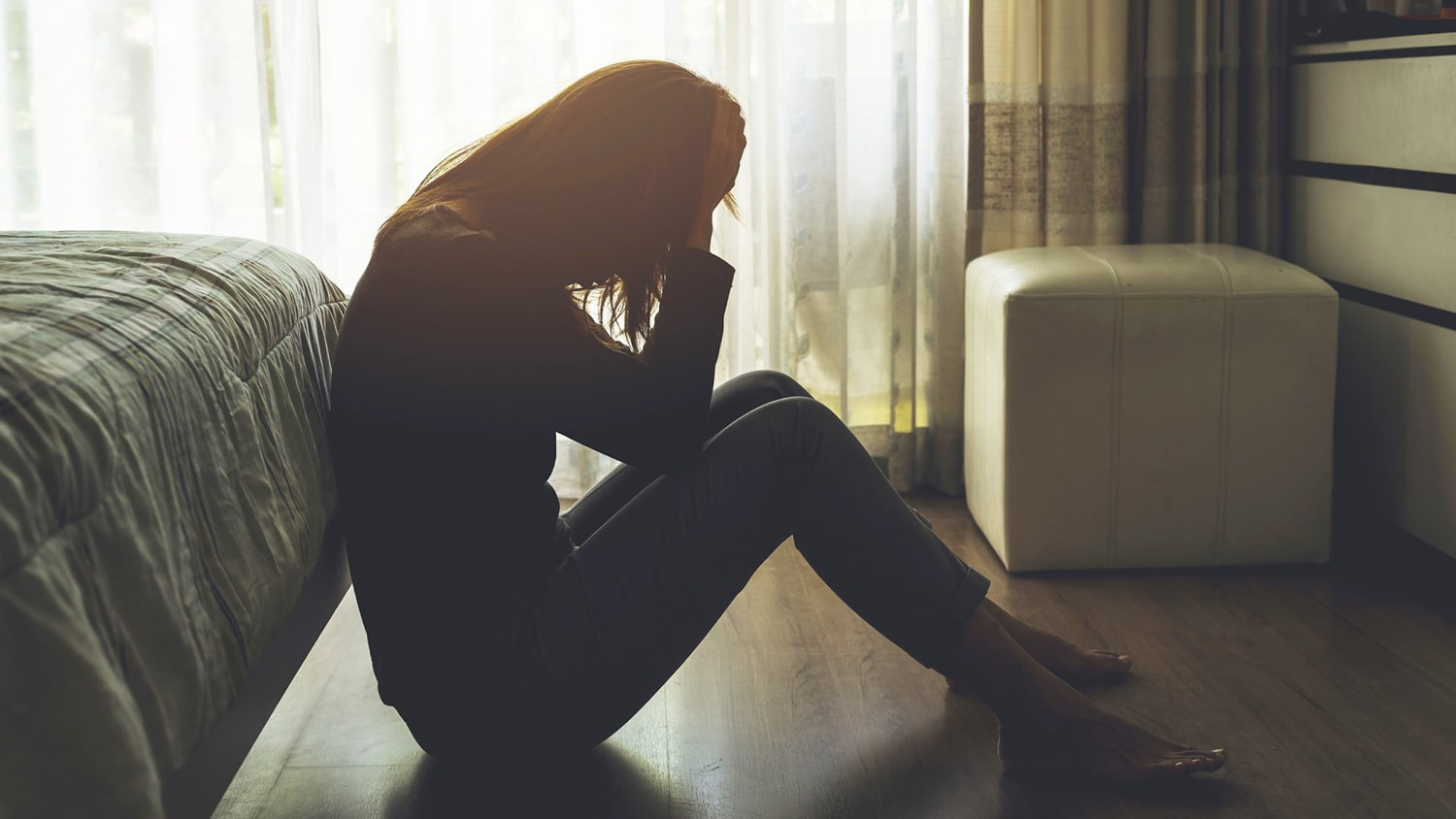
Depression is a complex mental health condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It goes beyond temporary sadness and can significantly impact a person’s daily life, relationships, and overall well-being. Understanding the most effective treatments for depression, its symptoms, and how family members can offer support is crucial in helping those affected find a path toward recovery.
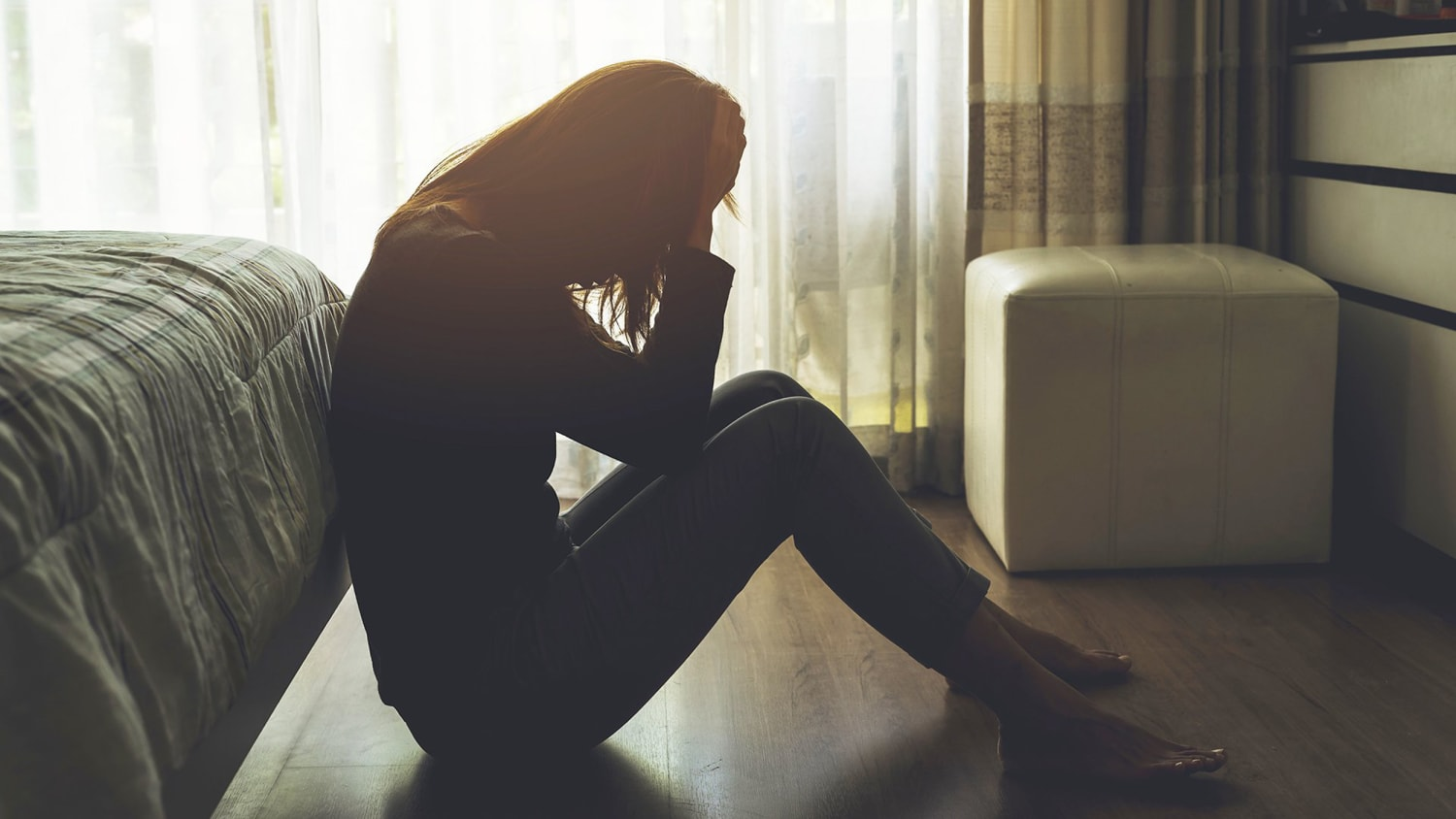

Recognizing the Symptoms of Depression
The first step in treating depression effectively is recognizing its symptoms. While depression can manifest differently in individuals, common symptoms include:
- Persistent Sadness or Low Mood: Feeling down, hopeless, or empty for an extended period.
- Loss of Interest in Activities: Lack of interest or pleasure in activities that were once enjoyable.
- Changes in Appetite or Weight: Significant weight loss or gain unrelated to dieting.
- Sleep Disturbances: Insomnia or excessive sleeping (hypersomnia).
- Fatigue or Lack of Energy: Feeling tired even after adequate rest.
- Difficulty Concentrating: Trouble focusing, making decisions, or remembering details.
- Feelings of Guilt or Worthlessness: Intense feelings of self-blame or worthlessness.
- Thoughts of Death or Suicide: Recurring thoughts about death, suicide, or self-harm.
These symptoms can vary in severity and duration. It's essential to seek professional help if you or a loved one exhibits several of these symptoms for more than two weeks.

The Most Effective Treatments for Depression
Effective treatment for depression often involves a combination of therapy, medication, lifestyle changes, and support from loved ones. Here are the most common and effective treatment approaches:
1. Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy is one of the most effective treatments for depression. CBT focuses on identifying and changing negative thought patterns that contribute to depressive symptoms. By challenging these thoughts and replacing them with healthier ones, individuals can develop coping strategies to manage their condition.
- Duration: Typically involves weekly sessions for 12-20 weeks.
- Benefits: Empowers individuals to control their thoughts, reduces depressive symptoms, and prevents relapse.
2. Medication (Antidepressants)
Antidepressants are commonly prescribed to treat moderate to severe depression. These medications help regulate brain chemicals (neurotransmitters) like serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine, which play a key role in mood regulation.
- Types of Antidepressants: Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs), tricyclic antidepressants, and monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs).
- Duration: It can take several weeks (4-6 weeks) for medications to show their full effect.
- Considerations: It’s crucial to follow a healthcare provider’s guidance and report any side effects or concerns.
3. Psychotherapy (Talk Therapy)
Talk therapy, such as interpersonal therapy (IPT) and psychodynamic therapy, provides a safe space for individuals to express their feelings, explore their emotions, and address the underlying causes of depression.
- Benefits: Helps individuals understand relationship dynamics, resolves conflicts, and develops healthier coping mechanisms.
- Duration: The length of therapy depends on the individual’s needs and the severity of their condition.
4. Lifestyle Changes and Physical Activity
Incorporating lifestyle changes is a complementary approach that can significantly improve mood and reduce symptoms of depression. Regular physical activity, a balanced diet, and adequate sleep are all crucial components.
- Exercise: Regular aerobic exercise like walking, jogging, or swimming boosts mood-enhancing chemicals (endorphins).
- Diet: Nutrient-rich foods that include omega-3 fatty acids, whole grains, and lean proteins can support brain health.
- Mindfulness and Meditation: Practices like yoga and meditation help manage stress and promote a sense of well-being.
5. Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT) and Other Advanced Treatments
For severe cases of depression that do not respond to traditional treatments, Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT) or Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) may be recommended.
- ECT: Involves electrical stimulation of the brain to relieve severe depressive symptoms.
- TMS: Uses magnetic fields to stimulate nerve cells in the brain, improving mood regulation.

Supporting a Loved One with Depression: A Guide for Family Members
Family support is a crucial aspect of the recovery process for someone dealing with depression. Here are some ways family members can offer meaningful support:
1. Educate Yourself
Understanding depression as a medical condition rather than a personal failure helps eliminate stigma and promotes a more compassionate approach.
2. Offer Emotional Support
Listen without judgment and acknowledge the person’s feelings. Simply being present and showing empathy can make a significant difference in their journey to recovery.
3. Encourage Professional Help
Encourage your loved one to seek professional help, such as therapy or medication. Offer to help them make appointments or accompany them to their sessions if they feel comfortable.
4. Create a Supportive Environment
Help create a supportive and low-stress environment at home. Encourage healthy habits like regular exercise, a balanced diet, and consistent sleep patterns to foster a positive atmosphere.
5. Be Patient and Understanding
Recovery from depression is a gradual process. It’s important to be patient and avoid placing pressure on your loved one to "snap out of it" or "move on."
The Treatment Process: What to Expect
The process of treating depression involves several stages, each tailored to meet the individual’s needs:
- Assessment and Diagnosis: A mental health professional conducts a thorough evaluation to diagnose the type and severity of depression.
- Treatment Plan: Based on the diagnosis, a personalized treatment plan is developed, which may include therapy, medication, or a combination of both.
- Regular Monitoring: Continuous monitoring of progress is essential to ensure that the treatment is effective. Adjustments may be made to the treatment plan if necessary.
- Long-Term Management: After initial recovery, ongoing management and regular check-ups are crucial to prevent relapse.

Conclusion
Depression is a serious but treatable mental health condition that requires a multi-faceted approach to manage effectively. With the right combination of therapies, medication, lifestyle changes, and a strong support system, individuals suffering from depression can achieve significant improvements in their mental well-being. Family members play an essential role in the healing process, offering the emotional support and encouragement needed for recovery. By understanding the symptoms, treatment options, and how to provide support, we can help create a compassionate environment for those on their journey to overcoming depression.